A mortgage loan can reshape a borrower’s financial future. As an originator, staying current on the different loan options is essential so clients can make informed choices.
One option that could be beneficial for many clients is Fannie Mae mortgages. These government-sponsored mortgages are heavily regulated and offer many advantages to qualified borrowers.
This ebook dives into the details of Fannie Mae mortgages, explaining what they are and the requirements for qualification. We’ll also discuss determining if a Fannie Mae loan is the right financing option for your clients.
Fannie Mae Loans 101
The Federal National Mortgage Association (FNMA), or Fannie Mae, was founded in 1938 as part of the New Deal legislation. It is a government-sponsored enterprise (GSE) that ensures mortgage lenders have access to capital and borrowers can get decent financing.
Fannie Mae purchases mortgages from originators and packages them into securities they sell to investors on the secondary market. This relationship helps provide lenders with liquidity, which in turn allows them to offer their customers more affordable mortgages with better terms.
Borrowers seek Fannie Mae loans because of the many benefits, including easier qualification standards. These mortgages can help you work with clients with less-than-perfect credit scores or limited down payment funds.
Fannie Mae Loan Requirements
Qualifying for a Fannie Mae loan means meeting specific criteria in the following categories:
Credit Score
Fannie Mae mortgage requirements demand a 620 or higher credit score for conventional home loans. However, some lenders may require a higher score.
Income
To qualify for a Fannie Mae loan, borrowers must have an income that meets program requirements. An advantage of Fannie Mae mortgages is that nontraditional income sources such as alimony and long-term disability are acceptable in some cases.
Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI)
Debt-to-income ratio gets calculated by dividing a borrower’s monthly recurring debts by their gross monthly income. Many lenders require that borrowers have a DTI of no more than 45%.
Employment History
Fannie Mae guidelines require most borrowers to have a consistent two-year employment history before applying for a loan. This requirement includes full-time, part-time, contract work, and self-employed individuals. Borrowers will also need to provide reasonable proof their income will continue for three years after closing the loan.
Exceptions can be made for borrowers whose “employment profile demonstrates that there are positive factors to reasonably offset the shorter income history.”
Property Eligibility
A Fannie Mae conventional loan is only available for specific properties such as family properties for residential use like single family homes, multi-family properties, condos, and townhomes. Ineligible properties include vacant lots, farms, and properties that can’t be occupied year-round.
Down Payment
Fannie Mae requires a minimum down payment of 3%; however, some lenders may require a higher amount.
Fannie Mae Loan Limits
The conforming loan limits established by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA) are the maximum loan amounts for Fannie Mae loans. The limits vary from area to area and fluctuate annually.
For 2023, baseline conforming loan limits for properties within the contiguous U.S. range from $726,200 for a single-unit home to $1,396,800 for a four-unit property. High-balance conforming loan limits range from $1,089,300 to $2,095,200. High-balance loans are designed for borrowers who live in high-cost areas. The baseline conforming loan limits for borrowers who reside in Alaska, Guam, Hawaii, and the U.S. Virgin Islands mirror the high-balance limits for the rest of the country.
To determine the loan limit where your borrower is located, use Fannie Mae’s map to determine the area’s median income.
Fannie Mae Loan Programs
Fannie Mae offers multiple loan programs with varying advantages and requirements.
HomeReady® Mortgage
HomeReady® mortgages help low- and moderate-income buyers purchase homes. The program allows borrowers to put as little as 3% down to qualify. The down payment can be comprised of funds from multiple sources, for instance, non-occupying relatives and friends. HomeReady® mortgages also have lower mortgage insurance premiums than other Fannie Mae loan programs.
For clients that are already homeowners, you can offer HomeReady as a valid refinancing option if they have at least 3% equity in the property.
HomeStyle® Renovation Mortgage
Borrowers can apply for a HomeStyle® Renovation mortgage to finance the costs of a home and its renovations. The purchase price gets sent at closing, but the funds reserved for repairs and renovations cannot be accessed until a licensed contractor sends plans to the bank. Inspections are performed to ensure the work gets completed as described.
97% LTV Options
Fannie Mae’s 97% LTV option lets borrowers purchase a home with as little as 3% down, creating a 97% loan-to-value (LTV) ratio. Unlike the similar HomeReady program, this program has no income cap. It is, however, only available to clients who are first-time homebuyers.
HFA Preferred
The HFA Preferred program is exclusively for borrowers working with a state or local housing finance authority (HFA). It offers lower mortgage insurance premiums, down payments as low as 3%, and closing cost assistance. The HFA sets income limits.
RefiNow
Fannie Mae RefiNow aims to help borrowers refinance their current mortgage at a lower interest rate. To qualify, borrowers need substantial home equity, an income at or below 80% of their area’s median income, and a solid payment history. Any credit score can qualify, a change introduced in April 2022.
Fannie Mae Loan Application Process
It’s important to note that Fannie Mae does not lend directly to borrowers; a lender must originate each loan. The process starts by applying for a new loan with a lender and getting approved. A borrower must provide income, tax returns, bank statements, pay stubs, and other documents specific to the loan program they are applying for.
Once all documentation is submitted, it goes through the processing and underwriting stage, where the lender evaluates the applicant’s creditworthiness. If the loan is approved, the next step is the closing process. During closing, a borrower will sign all documents and pay closing costs. The loan then goes through a final review at Fannie Mae to ensure compliance. After closing, the borrowers will receive their funds from the loan, and the lender may then choose to submit the loan for a Fannie Mae for sale or service the loan themself.
Fannie Mae Loan Servicing Guidelines
Loan servicers must follow specific guidelines set by Fannie Mae to maintain compliance with their standards. For example, they must provide payment plans and loss mitigation options when a borrower is having trouble making payments. Loan servicers must also follow Fannie Mae’s rules regarding late fees.
Loan servicers must stay aware of Fannie Mae’s servicing guidelines and ensure they comply. To help, Fannie Mae offers training courses, resources, and other materials accessible through their website.
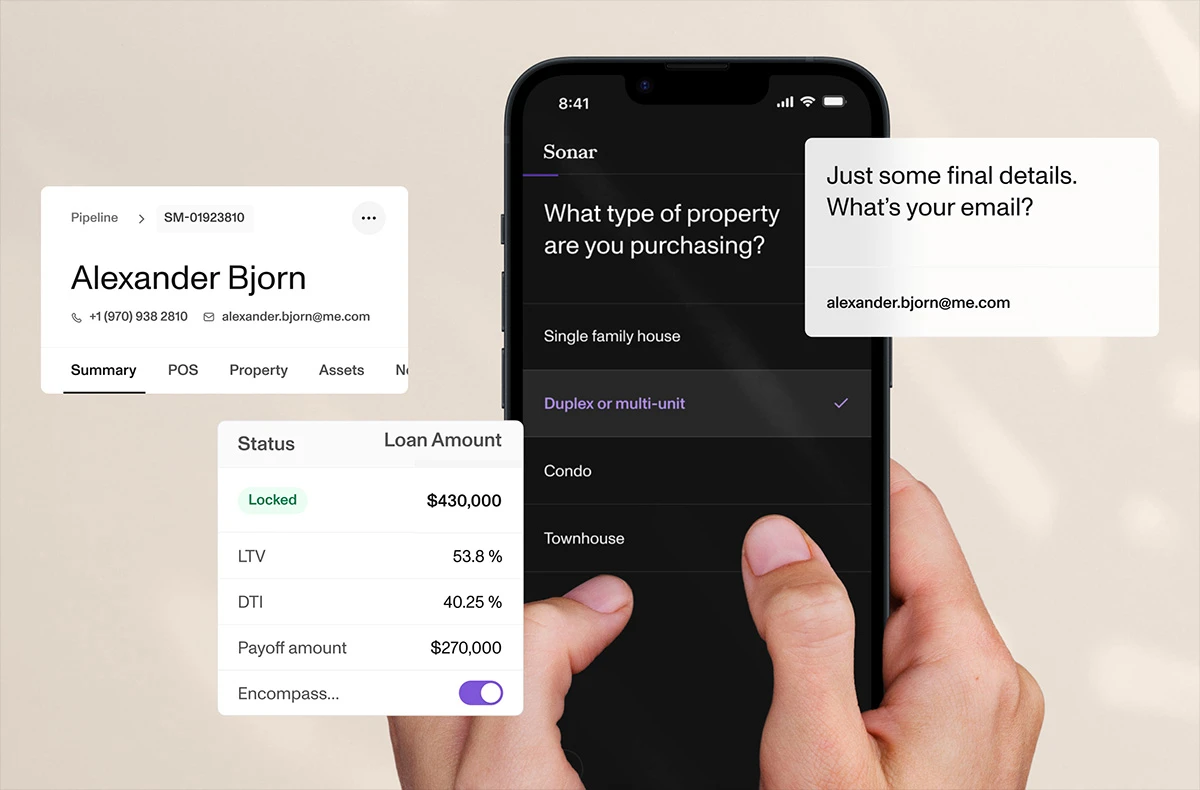
Sonar: Your All-in-One Loan Experience Platform
Sonar is a comprehensive platform for mortgage lenders and brokers that combines the power of LOS and POS systems to create a one-stop shop for loan origination and processing. Due to its streamlined process, Sonar allows lenders to originate and close Fannie Mae loans faster and more accurately than before.
With Sonar, users can access the tools they need throughout the loan cycle – from prequalification to closing. The platform includes features that support major Fannie Mae loan programs, including HomeReady and RefiNow.
Elevate your borrower experience and boost profitability with Sonar. Request a demo today.
Fannie Mae FAQs
Q: What’s the difference between Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac?
A: Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac are government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs) that provide liquidity to the mortgage market by buying mortgages from lenders. They both have similar programs for helping borrowers, but there can be significant differences in their loan terms and conditions.
Q: How do Fannie Mae loans compare to other types of mortgages?
A: Fannie Mae loans are conventional loans that typically have lower interest rates, overall less costs, and streamlined approval processes, making them more attractive to borrowers. They also require a lower down payment, offer more generous income limits, and provide options for first-time homebuyers.
Q: How can I help my borrowers qualify for a Fannie Mae loan?
A: Work with your borrower to ensure they meet the requirements to qualify, such as having a minimum credit score or sufficient income. Help them understand the different loan programs available and provide guidance on selecting the best one.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when originating a Fannie Mae loan?
A: Be sure you fully understand the various loan requirements and that all documentation is accurately completed and submitted on time. Ensure you’re aware of any changes introduced, such as new underwriting guidelines, low down payment options for first-time home buyers, or recent income limits.